系統建立IPC通訊(如消息隊列、共享內存時)必須指定一個ID值。通常情況下,該id值通過ftok函數得到。
ftok原型如下:
key_t ftok( char * fname, int id )
fname就時你指定的文件名(該文件必須是存在而且可以訪問的),id是子序號,雖然為int,但是只有8個比特被使用(0-255)。
當成功執行的時候,一個key_t值將會被返回,否則 -1 被返回。
在一般的UNIX實現中,是將文件的索引節點號取出,前面加上子序號得到key_t的返回值。如指定文件的索引節點號為65538,換算成16進制為 0x010002,而你指定的ID值為38,換算成16進制為0x26,則最後的key_t返回值為0x26010002。
查詢文件索引節點號的方法是: ls -i
以下為測試程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#define IPCKEY 0x11
int main( void )
{
int i=0;
for ( i = 1; i < 256; ++ i )
printf( "key = %x\n", ftok( "/tmp", i ) );
return 0;
}
在成功獲取到key之後,就可以使用該key作為某種方法的進程間通信的key值,例如shmget共享內存的方式。
shmget的函數原型為
int shmget( key_t, size_t, flag);
在創建成功後,就返回共享內存的描述符。在shmget中使用到的key_t就是通過ftok的方式生成的
實例:
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 1024
extern int errno;
int main()
{
int shmid;
char *shmptr;
//創建共享內存
if((shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, SIZE, 0600)) < 0)
{
printf("shmget error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//將共享內存連接到 可用地址上
if((shmptr = (char*)shmat(shmid, 0, 0)) == (void*)-1)
{
printf("shmat error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
memcpy(shmptr, "hello world", sizeof("hello world"));
printf("share memory from %lx to %lx, content:%s\n",(unsigned long)shmptr, (unsigned long)(shmptr + SIZE), shmptr);
//拆卸共享內存
if((shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) < 0))
{
printf("shmctl error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
}
多進程之間共享內存情況:
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define SIZE 1024
extern int errno;
int main()
{
int shmid;
char *shmptr;
key_t key;
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
printf("fork error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
sleep(2);
if((key = ftok("/dev/null", 1)) < 0)
{
printf("ftok error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if((shmid = shmget(key, SIZE, 0600)) < 0)
{
printf("shmget error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
if((shmptr = (char*)shmat(shmid, 0, 0)) == (void*)-1)
{
printf("shmat error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
//memcpy(shmptr, "hello world", sizeof("hello world"));
printf("child:pid is %d,share memory from %lx to %lx, content:%s\n",getpid(), (unsigned long)shmptr, (unsigned long)(shmptr + SIZE
), shmptr);
printf("child process sleep 2 seconds\n");
sleep(2);
if((shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) < 0))
{
printf("shmctl error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
exit(0);
}
//parent
else
{
if((key = ftok("/dev/null", 1)) < 0)
{
printf("ftok error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if((shmid = shmget(key, SIZE, 0600|IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL)) < 0)
{
printf("shmget error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
if((shmptr = (char*)shmat(shmid, 0, 0)) == (void*)-1)
{
printf("shmat error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(shmptr, "hello world", sizeof("hello world"));
printf("parent:pid is %d,share memory from %lx to %lx, content:%s\n",getpid(),(unsigned long)shmptr, (unsigned long)(shmptr + SIZE
), shmptr);
printf("parent process sleep 2 seconds\n");
sleep(2);
if((shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) < 0))
{
printf("shmctl error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
}
waitpid(pid,NULL,0);
exit(0);
}
輸出為:
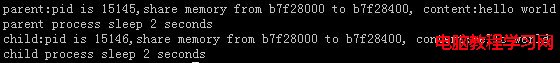
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0)的作用是從系統中刪除該恭喜存儲段。因為每個共享存儲段有一個連接計數(shmid_ds結構中的shm_nattch),所以除非使用該段的最後一個進程終止與該段脫接,否則不會實際上刪除該存儲段